What is Hard and Soft Water?
Consistent hydration provides a variety of positive health effects. 1 However, did you know that the type of water you consume has an impact on your health as well?
The amount of minerals in water determines whether it is “soft” or “hard.” Calcium, magnesium, and other essential minerals will be present in larger concentrations in hard water, whereas sodium will be present in higher concentrations in soft water (salt).
Both soft and hard water are regarded as safe to drink, however, regularly ingesting either form of water has advantages and disadvantages.
What’s The Difference Between Hard Water and Soft Water?
You could believe that the water that flows from your tap in its natural state is the same no matter where you live and whether it is hard or soft. This is not the case, though.
There are two categories of water: hard water and soft water. The difference is based on how many dissolved minerals are present in the water. Calcium and magnesium are abundant in hard water, whereas they are absent or very little in soft water. Soft water typically has higher concentrations of sodium or salt than it does of calcium and magnesium.
The amount of minerals present determines the definition of “hard water.”
Hardness is defined as a concentration of more than 60 milligrams per liter of water. Water that is very hard can contain up to 180 milligrams per liter. You should anticipate mineral buildup affecting your appliances at these levels.
Where Hard Water Originates
The quantity of dissolved minerals in the water, notably calcium and magnesium, is used to determine the hardness of the water. People that utilize groundwater for their water systems frequently have water with greater hardness levels because the water naturally picks up trace amounts of these minerals as it passes through soil and rock.
Homeowners who live in areas with hard water may find that when the water is heated, calcium carbonate deposits can solidify. This can shorten the useful life of equipment, decrease the effectiveness of electric water heaters, and increase the cost of heating water.
The most trustworthy information regarding your water hardness levels can always be found from your local health agency or local water utility business, even if water hardness levels vary based on your water treatment system and where you reside. For instance, if you drink water from Los Angeles, it may be wise to consider getting a water filter system.
Is it Better To Drink Hard or Soft water?
Rainwater is gentle by nature and falls softly. Water, however, gathers up minerals like chalk, lime, and mostly calcium and magnesium as it travels through the earth and into our rivers, turning it into hard water.
Because it includes necessary minerals, hard water is occasionally favored as drinking water. because of the flavor as well as the health advantages. It is not harmful to your health to drink hard water instead of soft water.
In fact, the National Institutes of Health have discovered that drinking hard water is beneficial to one’s health because calcium and magnesium are essential for improved heart function, digestion, blood sugar regulation, and even the prevention of cancer. Additionally, hard water can taste better as minerals improve water’s taste.
However, people who may be on a low salt diet or those who have heart or circulation issues are not advised to drink soft water. As minerals are eliminated during the softening process, the salt concentration rises.
According to research, the risk of cardiovascular disease is lowest in regions with high mineral water concentration. There are techniques to deal with the salt in soft water, giving homes access to the finest possible water for cleaning requirements as well as better-tasting water. They are deionization, distillation, and reverse osmosis.
Since calcium and magnesium do not pose any health risks and can help build stronger bones, Indiana American Water does not soften the water. On the other hand, removing these elements using sophisticated methods can raise the salt levels in the water, which might be dangerous for people with high blood pressure.
Is it OK To Drink Hard Tap Water?

Yes, hard water has additional health advantages. The body requires the minerals calcium and magnesium for the development and maintenance of bones and muscles.
Additionally, these minerals control how enzymes function and blood pressure. These minerals may be found in hard water, which is consumed.
However, there is a workaround if you don’t want the negative impacts of hard water on your house. Many experts feel that hard water is superior to soft water for ingestion.
However, we shouldn’t discount the advantages of soft water. Due to this, many industry professionals advise employing a water softener with a water bypass valve system.
As a result, hard water will be able to flow to select particular locations where it may be utilized for drinking and cooking. If not, we advise you to consume water from alternative sources, such as bottled water.
What happens if the Water is Too Hard?

The most obvious distinction between hard and soft water may be recognized while performing routine chores when the water is boiling. Hard water is the cause of stained dishes, streaky dishes, and baths covered in soap scum and film.
Due to the soap’s response to the magnesium and calcium, the lather is not as thick and bubbly, making it less effective. Even hair cleaned in harsh water might seem dull and feel sticky. Household appliances might suffer from hard water damage and use more energy.
Hard water minerals can also alter the pH balance of your skin, decreasing its defenses against pathogenic microorganisms and illnesses. Eczema sufferers may be particularly at risk.
You turn on the water to wash your hands and fill the tub for a bath, but your water’s quality can be having an impact beyond your personal hygiene when it comes to hard or soft water.
Your energy consumption may also be impacted by the hardness of your water or the quantity of calcium or magnesium that has been dissolved in it. Your appliances may even need to work harder as a result of hard water.
For many people, the choice between soft water and hard water comes down to price. Costs associated with mineral-saturated water include lost energy, wear and tear, inefficient operation, early appliance failure, and shortened pipe lifespan.
Environmental harm can also result from increased chemical use to combat the consequences of hard water. All things considered, hard water can be expensive.
What are the benefits of soft water?
Soft water will be a favorite among household workers since it truly makes duties more productive. Items will be left cleaner and soap will lather better. Hair will seem healthy, and glasses will glitter. There won’t be any gunk on the shower curtain. Skin and clothing are left softer.
In addition to saving time, using fewer soap and detergents will result in cost savings. Soft water can also increase the lifespan of washing machines, dishwashers, and water heaters since they don’t have to work as hard.
In homes with water softeners, energy costs are considerably reduced. This is something to think about in an era where energy prices are steadily rising.
What is Water Softening?
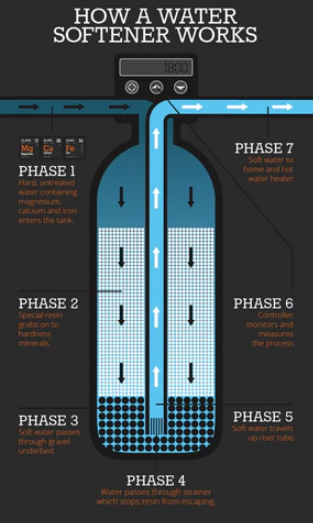
Hard water is passed through resin beads containing positively charged sodium and potassium ions in typical water softener systems to soften the water. As the resin beads draw in the calcium and magnesium ions, which are also positively charged, the sodium and potassium are released into the water. This exchange produces softened water with trace levels of salt and potassium.
The advantages of water softeners include cleaner laundry, more durable appliances, and less soap residue. Laundry detergent and other cleansers and detergents are used less often by consumers. Clothing is more vibrant, and cleaning sinks, tubs, and showers is easier.
Boilers, water heaters, and dishwashers all operate more effectively and require less maintenance when using soft water because it prevents scale accumulation in pipes and plumbing fixtures. Soft water consumers frequently say that their skin and hair feel less flaky and dry.
Do I Need a Water Softener?
If you’ve been using hard water for a time, you might not be aware of the negative impacts. Not sure if your water has to be softened?
A coating of scum on hair and skin after washing is one of the telltale indications. Other warning signs include film or spots on your dishes, appliances, and clothing, scale buildup or mineral buildup around faucets or in appliances, dull, flat hair, or dry and itchy skin.
An essential first step in controlling energy consumption and the influence of water on your house and daily life is to test your water to find out if it is hard or soft.
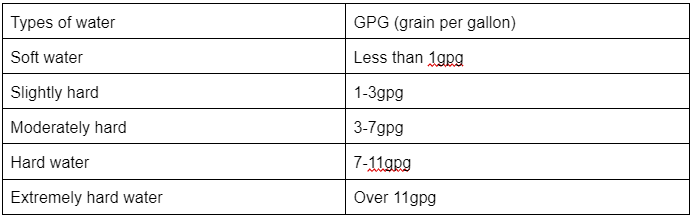
Hard water is defined as having dissolved mineral hardness of 1 GPG (grains per gallon) or greater, according to the Water Quality Association of the United States. Here is a useful table that displays how hard the water is:
Water Softener 101
The magnesium and Calcium that are present in hard water are removed by a water softening system and replaced with sodium ions, claims Scientific American. Ion exchange is the mechanism that causes this to happen.
Typically found in your plumbing system, water softeners function by reversing the process through which water gets hard. When moving through soil in a ground system, a water molecule’s polarity permits it to pick up mineral ions; however, a water softener reverses this by drawing the mineral content back out of the water.
A water softening system in water softener consists of two tanks: the brine softener tank and the resin (also known as mineral) tanks.
The action takes place in the resin tank as sodium ions from the brine solution swap places with the hard water’s mineral ions. Following the collection of all the hard mineral ions, the tank is flushed with potassium chloride or sodium chloride.
Compare Drinking Hard and Soft Water
Your preference will determine whether you like the flavor of hard or soft water. We have lots of acquaintances that fit either description here at American Home Water and Air.
As a result, choosing between drinking soft water and hard water is more about your health than it is about the flavor of drinking water for both hard and soft water.
The good news is that, as far as eating substances, calcium and magnesium are safe for you. These two minerals, after all, are principally responsible for the hardness of water. They do have some adverse consequences on the outside world.
For the majority of healthy people, drinking soft water is also extremely safe. The high salt content that is typical of soft water tends to worry people. The amount of salt in soft water is actually just marginally higher and is not dangerous for healthy persons.
Consult your doctor if you have a disease that might be exacerbated by consuming more salt. Some medical professionals may advise against consuming softened water. If that’s the case, a special faucet that avoids the softener can be fitted. In this manner, your other appliances and fixtures will receive soft water while the water you use for drinking and cooking remains unsoftened.
Hard Water vs Soft Water For Hair
Here is when the main drawbacks of hard water start to emerge.
When you shower, calcium and magnesium both harm your hair, making it fragile. Additionally, you’ll discover that your shampoo won’t fully lather, leaving a film on your scalp and hair.
Shampoos predominantly consisting of synthetic detergents may prevent this, but they still risk causing harm to your hair.
When comparing soft water to hard water for hair, the latter is clearly superior. Your hair suffers damage from hard water, which makes it difficult to adequately clean. Using a water softener is the best method to prevent this.
Difference On Skin
Hard water has comparable effects on your skin and hair as it does on your hair. Your skin will get dry and develop a layer of film as a result of mineralization, which undermines your hygiene.
According to research, those who already have eczema may become more sensitive to it or develop it as a result of using hard water. Because of how susceptible children are, families face a serious risk from hard water.
When comparing the effects of soft vs. hard water on skin, soft water once more demonstrates its advantages. It lacks the minerals that might otherwise result in eczema and other skin conditions.
There is no escaping the increased risk of eczema, even though some of these effects (specifically the film that forms on your skin) can be avoided by using a more abrasive soap. The only solution for you is a water softener.